VisCli
Highly efficient! - Instrument to strengthen our vision for the climate
VisCli - the new generation of servers
Data centres are real powerhouses that require an immense amount of energy to operate servers, process data and store information.
However, a large proportion of this energy is used to cool the servers. It is estimated that up to 40% of a data centre's total power consumption is used for air conditioning. This is not only a financial burden, but also has a significant impact on the environment.
To counteract this, companies need to find innovative solutions to increase their energy efficiency.
Innovative solutions to increase efficiency
1. virtualisation and cloud computing
The virtualisation of servers enables companies to operate several virtual machines on one physical server. This reduces the need for physical hardware and significantly lowers energy consumption. Cloud computing also offers the possibility of scaling resources according to demand and thus avoiding overcapacity.
2. Efficient cooling systems
The implementation of modern cooling systems can drastically reduce energy consumption. Technologies such as free cooling utilise the outside temperature to cool the server rooms and thus reduce the use of energy-intensive air conditioning systems. In addition, intelligent cooling systems can optimise the airflow and avoid hotspots in the data centre.
3. Use of renewable energies
More and more companies are turning to renewable energies such as solar or wind power to cover their electricity needs. There are already numerous initiatives to promote renewable energy. By using green energy, data centres can not only reduce their CO2 emissions, but also lower their operating costs in the long term.
4. Monitoring and management of energy consumption
Effective energy management is essential in order to optimise power consumption in data centres. By using monitoring tools, companies can monitor their energy consumption in real time and take targeted measures to reduce consumption. Data analyses help to identify and improve inefficient processes.
Our approach
Combination of energy-saving but powerful components with virtualisation technology
The optimised selection of components and the arrangement of the VisCli boards result in very low heat generation.
On the way to sustainable IT
Energy efficiency in data centres is not just a technical problem, but a social issue. Companies are faced with the challenge of making their IT infrastructure more sustainable while remaining competitive. Through innovative approaches such as virtualisation, efficient cooling systems and the use of renewable energies, we can make a joint contribution to reducing electricity consumption.
The challenges are great, but the opportunities are even greater. Let's work together towards an energy-efficient future - for ourselves and for generations to come. By optimising our data centres and adopting sustainable practices, we can not only reduce our operating costs, but also minimise our environmental footprint.
It's up to all of us to drive this change!
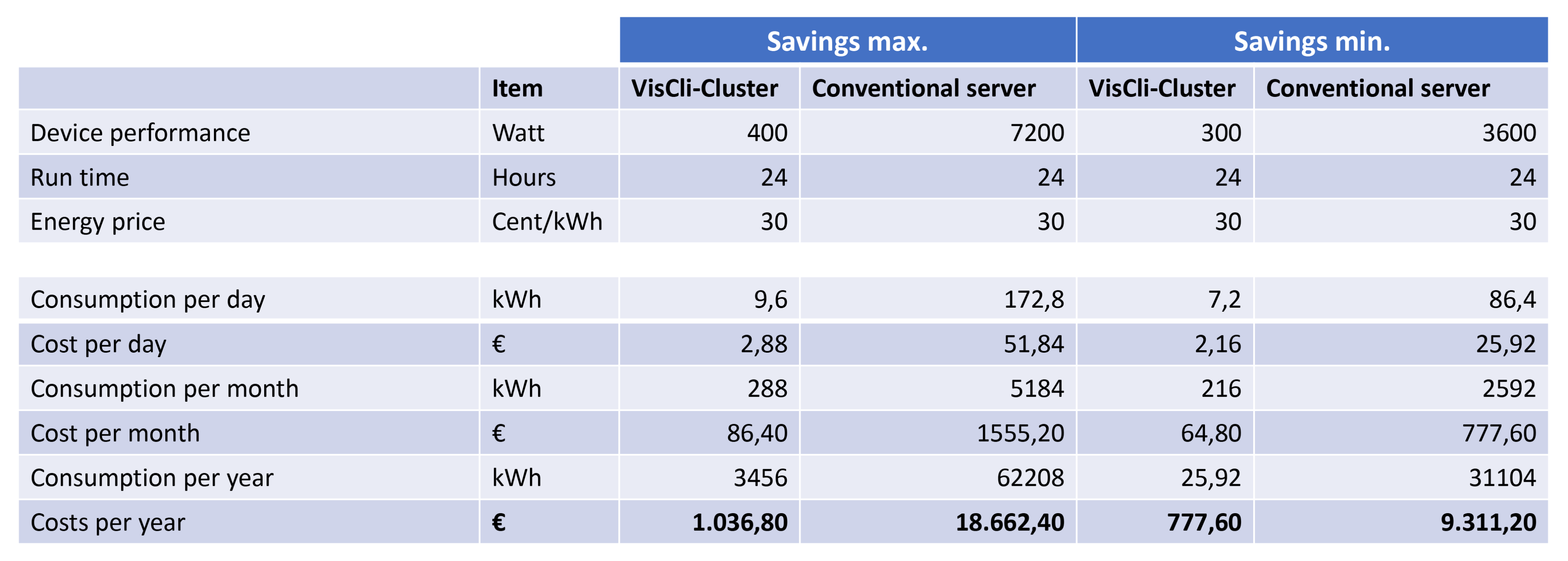
Calculation
VisCli cluster and conventional server in comparison
The VisCli board consumes approx. 65 watts under full load, but only approx. 45 watts on average in normal operation.
For a VisCli cluster with 6 VisCli boards, this corresponds to an average power consumption of 300 watts rounded up and 400 watts rounded up under full load.
Usually, a conventional server requires at least 600 watts and 1200 watts under maximum load, i.e. a cluster with conventional components requires 3600 watts and a maximum of 7200 watts for 6 servers.